What does CNC machining defect mean?
CNC machining defects are any undesirable results and failures in the finished product of a machining process. This includes Physical damage to the workpiece, dimensional errors, poor surface finish, material defects, broken tools, machine failures, and more.
Undesirable machining defects may lead to glitches in the final result of the machined part. It can lead to dimensional errors, low quality surface finish, heat generation and many more problems.
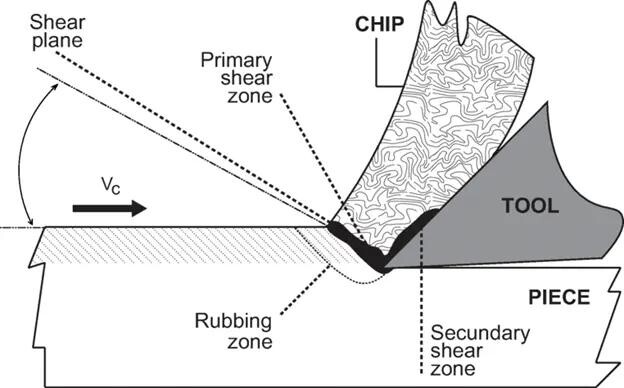
The root causes of cutting machining defects are chips, chatter, burrs, chipping, and chip tumors. Since these defects are caused by “cutting metal with a tool” Even if the type of machine tool or machining method changes, such as machining centers, CNC lathes, automatic lathes, etc., the mechanism by which the defects are created does not change.
1.Chip formation defects:
Chips are the pieces or material that are created when a cutting tool removes material from a workpiece. Chip formation is an integral part of subtractive manufacturing because this is how material removal transforms the raw material into the desired shape. Chips need to be removed smoothly and continuously. Failure to remove them adequately can lead to machining defects and temporary stoppages, so they need to be reliably discharged.
There are many types of metal chips: spattered powder, continuous, discontinuous, curly, filamentary, long spirals, and more. Since the shape varies depending on the machining method and workpiece, it is no exaggeration to say that the quality of machining can be judged by looking at the chips.
How can I ensure that machining defects caused by chips are present?
- Chips are wrapped around the tool and there are too many chips in the machining area.
- Chips are caught when changing workpieces.
- If the cutting tool breaks unexpectedly, this may indicate that chips are causing the defect.
- If the machining process stops frequently or encounters unexpected stoppages.
- The drill bit breaks due to clogging of chips while drilling.
Prevention
- Use sharp and adequately maintained cutting tools. It will reduce the force required to cut the material and help prevent chip formation.
- Use proper cutting speed and feed rate. If the cutting speed is too slow, the tool will rub against the workpiece, generating heat and potentially causing chips. In addition, cutting too fast limits the removable rate because it cannot remove material fast enough.
- Use chipbreakers and chip removal tools.
2.How to ensure machining defects caused by chatter?
- Significant vibration during machining, accompanied by a loud rhythmic noise.
- Deterioration of the surface finish of machined parts
- Damage to machines and tools
- Reduced machining accuracy.
- Surface defects on the workpiece, such as scratches or pockmarks.
Prevention
- Using a tool with a positive rake angle prevents chatter by reducing cutting forces.
- Ensure that the foundation of the CNC machine is stable.
- Ensure that there is no looseness or play in the installation.
- Maintaining perfect tool alignment Tools with chamfered or rounded edges can reduce the risk of chatter by absorbing vibrations.
3.Defects caused by excessive burrs
Burrs are tiny, sharp protrusions or edges left on the surface of a machined part. These are essentially uncut protrusions in the piece and chips are pushed out. It is no exaggeration to say that the cutting process always produces burrs ranging from large to small burrs.
If a burr is retained outright, it can cause trouble or injury in subsequent processes, so machining and reliable deburring that inhibits burr generation is critical.
Poor surface finish is the number one defect that forms burrs during CNC machining. Other defects include poor product quality, increased scrap and waste, and increased production time.
How do you ensure that machining defects are caused by excessive burrs?
- Burrs are visible on the machined surface.
- Rough surface with many defects.
- Poor fit and function
- Outflow of defective products.
Prevention
- Use the appropriate cutting tool for the material you are machining.
- Consider using a deburring tool to remove burrs created during machining.
- Tools with longer tip radii may prevent burr defects.
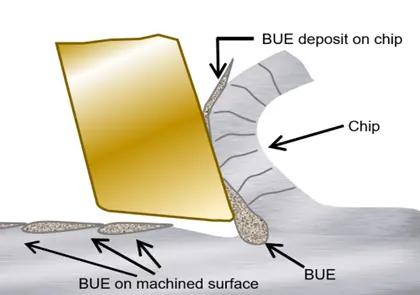
4.Chip Tumor(BUE) Defect
BUE is a phenomenon in which chips adhere to the tip of the cutting edge due to high cutting pressure and frictional heat.
The main causes of BUE are inappropriate cutting speeds and feed rates, inappropriate coolants or lubricants, and poor tool conditions and geometry. In addition, certain materials are susceptible to chip-accumulation problems, such as ductile materials that tend to work-harden (mild steel, brass, stainless steel, aluminum, etc.), which tends to produce chip-accumulation.
Accumulated edges can lead to poor fit and function, rough surface finishes, safety issues and dimensional inaccuracies.
How can I ensure that I avoid machining defects caused by chip-accumulation(BUE)?
- Tip cutting
- Visible BUE on the workpiece.
- Unexpected machine downtime.
- Poor fit and function
Prevention:
- Use tools with damping coatings or damping geometries.
- Use appropriate lubricants and coolants.